Hosting in Cloud Computing
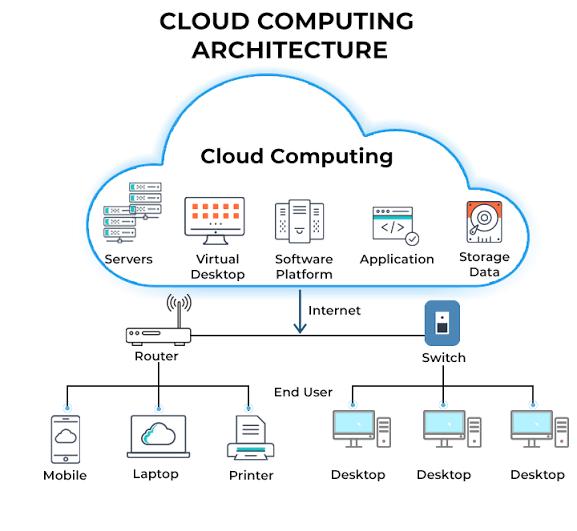
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals host applications, websites, and services. Hosting in cloud computing refers to using virtualized resources on remote servers rather than relying on traditional physical servers or on-premises infrastructure. This approach allows for better scalability, reliability, and cost efficiency while ensuring seamless access to computing resources over the internet.
Understanding Cloud Hosting
In traditional hosting, applications and websites are hosted on dedicated or shared physical servers located in data centers. However, cloud hosting eliminates the need for physical infrastructure by utilizing cloud service providers’ virtualized environments. Cloud hosting distributes resources across multiple servers, ensuring high availability, redundancy, and flexibility.
Cloud hosting is widely used for various applications, including web hosting, database management, software deployment, and large-scale enterprise solutions.
Types of Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is categorized into different models, depending on how resources are managed and accessed:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet.
- Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networking services.
- Examples: Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- PaaS offers a development environment for building, testing, and deploying applications.
- Developers don’t need to manage infrastructure; they focus on application development.
- Examples: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, Heroku.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
- SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis.
- Users can access applications via web browsers without installation.
- Examples: Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Dropbox.
Advantages of Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting provides several benefits over traditional hosting models:
Scalability:
- Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads.
Cost Efficiency:
- Pay-as-you-go pricing eliminates the need for large upfront investments.
- Reduces hardware and maintenance costs.
High Availability and Reliability:
- Cloud providers ensure uptime through redundant server networks.
- Data is backed up across multiple locations.
Security:
- Cloud providers implement robust security measures, including encryption and firewalls.
- Compliance with industry standards enhances data protection.
Accessibility and Flexibility:
- Access applications and data from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Supports remote work and collaboration.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance:
- Cloud providers handle updates, security patches, and server maintenance.
- Reduces IT management workload.
Challenges of Cloud Hosting
Despite its advantages, cloud hosting has some challenges:
Internet Dependency:
- A stable internet connection is required for seamless access.
Security and Compliance:
- Sensitive data must be protected against cyber threats.
Cost Management:
- Improper resource allocation can lead to unexpected costs.
Limited Control:
- Users rely on cloud providers for infrastructure management.
 logo
logo